A Brief Introduction to Hydrostatic Head / Pressure Test
In recent years, with the popularity of outdoor activities, consumers’ demand for textiles with waterproof and splash proof properties has greatly increased. The hydrostatic pressure resistance index is one of the important indicators for waterproof and breathable fabrics.
Contents
What is Hydrostatic Pressure Test?
Hydrostatic Pressure Test is to determine the resistance property to water penetration of fabric and material such as canvas, tarpaulin, manta, tent cloth, rain-proof garments.
During testing, the hydrostatic pressure increasing at a constant rate is applied from below the test specimen, whilst firmly clamped in the test head of 100cm2 area, until penetration water-drop occurs in three places. Record the pressure at the moment water first appears at the third place in the specimen.
Why does Hydrostatic Head Test Matter?
Ensure product quality: Fabrics, especially outdoor material, must have good water resistance property. Through hydrostatic head test, the producer can evaluate whether they meet the needed standard for waterproof performance, which help to prevent product failures.
Comparing Materials: By using the same testing methods and machine, producers can compare the water resistance of different fabrics and help them make decisions about which materials to use in their products.
Regulatory compliance: In many cases, producers need to meet certain regulatory requirements regarding the water resistance of their products. Through standard hydrostatic head test, producers can ensure that their products meet these requirements and avoid any potential legal or regulatory issues.
Hydrostatic Pressure Test Standards
The hydrostatic head test is a standardized procedure used to evaluate the water resistance of fabric and materials. Several test standards ensures the consistency, accuracy, and reliability throughout distinctive industries and applications. A number of the maximum usually referenced test standards (also known as waterproof testing standards) contains:
ISO 811: This International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standard identifies the technique for determining the resistance of fabric to water penetration using a hydrostatic pressure test. It outlines the apparatus, sample preparation, test procedure, and calculation approach for figuring out the hydrostatic head score of textiles.
IS L 1092: This Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) states the approach for determining the resistance of textiles to water penetration underneath hydrostatic pressure. It provides guidelines for sample preparation, test conditions, and calculation techniques to assess the waterproofing belongings of fabric used in varied applications.
AATCC Test Method 127: It is published by the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC); this technique outlines the process for determining the resistance of a fabric to water penetration with the use of a hydrostatic pressure test. It covers pattern instruction, test circumstances, and calculation strategies for determining the hydrostatic head rating of textiles.
ASTM D751: Developed by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), this widely covers the determination of hydrostatic resistance of fabrics coated with rubber or plastics. It gives guidelines for pattern preparation, test conditions, and calculation approaches to evaluate the waterproofing properties of substances utilized in rainwear, tents, and different outdoor equipment.
BS EN 20811 / ISO 811: This European standard, additionally followed through ISO, specifies a hydrostatic pressure test technique for assessing the water resistance of fabrics. It presents exact commands for undertaking the test, including sample conditioning, apparatus setup, test process, and calculation of hydrostatic head values.
EN 20811: This European standard agrees the test method for defining the resistance of a material to water penetration is done by the custom of a hydrostatic strain test. It includes pattern practice, device setup, test method, and intention methods for defining the hydrostatic head rating of fabrics.
GB/T 4744: This standard specifies the method for determining the water resistance of fabrics using a hydrostatic pressure test.
FZT 01004: This standard specifies the method for determining the water penetration resistance of fabrics using a hydrostatic pressure test.
How to Perform a Hydrostatic Test
4.1 Provide freshly distilled water for each specimen tested. If the instrument used is of the type in which the water to be used for testing is contained in the testing head and rises to come into contact with the specimen, the surface of the water in the testing head may be cleaned in one of the following ways, stated in order of preference.
- Empty the testing head and refill with sufficient freshly distilled water.
- Allow the distilled water to overflow from the testing head(s) so that the surface of the water is cleared. Sweep the surface of the water with a glass slide freshly coated with paraffin wax.
- Allow the distilled water to overflow from the testing head so that the surface of the water is cleared.
4.2 Wipe all the water from the clamping surfaces, Clamp the conditioned specimen in the test head so that the face of the fabric will be in contact with the water, The clamping shall be carried out in such a way that water will not be forced through the specimen prior to the start of the test, Subject the specimen immediately to increasing water pressure. Watch continuously for evidence of penetration by water.
4.3 Record the pressure, as centimeters or millibars of water, at which water first appears at the third place in the specimen. If agreed between parties, the appearance of the first drop can be reported and shall be stated in the test report, The accuracy for recording the pressure shall be as noted in table 1.
4.4 Do not take into account very fine droplets which do not grow after being formed. Count subsequent drops which penetrate through the same place in the fabric as one drop. Note whether the penetration of water occurs at the edge of the clamp and reject as unsatisfactory any test in which such penetration occurs. Test further specimens until reproducible results are obtained.
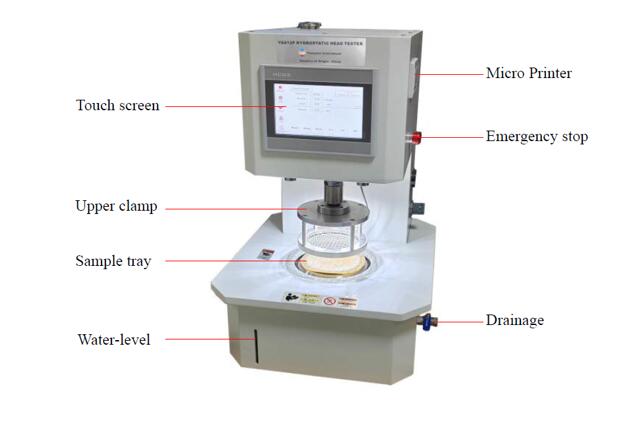
YG812P Hydrostatic Head Tester
Structures

Key Specifications
| Water pressure resolution | 1/10000 |
| Sensor accuracy | ≤1% |
| Test area | 100cm2, 7.8cm2(optional) |
| Pressurizing rate | 1KPa~100KPa/min (adjustable) |
| Test method | P. Rise, Constant P. & Timing, Constant P. & Time, Water Penetration, Fatigue |
| Display | Colorful touch screen |
| Printer | Thermal micro printer |
| Power supply | AC 220V±10%, 50Hz, 500W |
| Dimensions | 550×430×630mm |
| Weight | 60kg |
Software Interface
Instead of operating through touch screen, YG812P Hydrostatic Head Tester is equipped with a specially designed software, which can real-time display the pressure, water-drop appearance times, curve and statistic data.
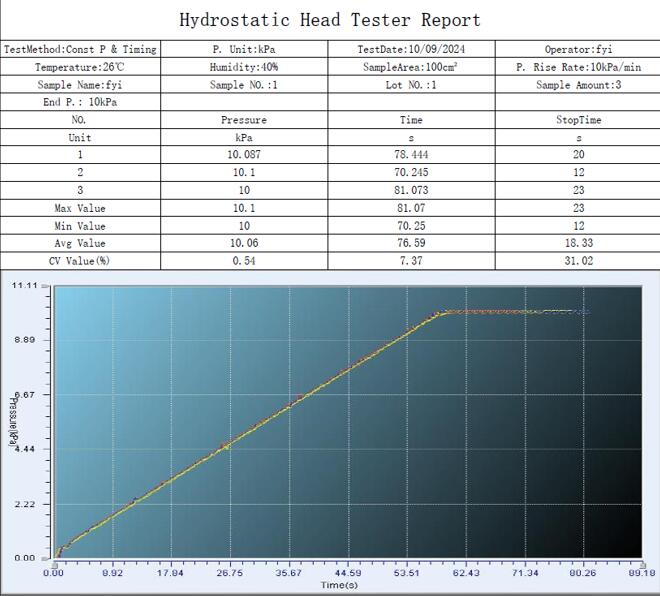
Test report
Here is a sample of test report which uses “Constant P. & Timing” method. It contains time-pressure curve, data record of each tests and statistic data (such as Max. value, Min. Value, Avg. value and CV% value).