
A Detailed Guide to Light Fastness Testing
Color accuracy and performance are two of the most important factors for manufacturers. From plastics to fabrics, the durability and longevity of color is the single most important indicator of quality.
Most products are designed for outdoor environments, where they are constantly exposed to the sun, especially textiles.
If a product fades under the sun, it might be a reason to stop production, but most items are already sold by then. Light fastness testing helps anticipate and prevent these product recalls ensuring quality.
This guide breaks down light fastness testing, standards of color fastness to light test, and applications of a tester like the YG611M.
Contents
- 1 What Is Light Fastness Testing?
- 2 Light Fastness Testing Methods
- 3 How Light Fastness Testing Works
- 4 What Factors Influence Light Fastness
- 5 Most Reliable Light Fastness Test: Xenon Arc Testing
- 6 Standards of Colorfastness to Light
- 7 Light Fastness Testing Solutions at Your Facility | Xenon Arc Tester YG611M
- 8 Applications of Lightfastness Testing
- 9 Key Features of Air Cooled Xenon Arc Tester YG611M
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 Common Questions about light fastness testing
What Is Light Fastness Testing?
Light fastness testing is a way to test the resistance of pigment (color) in a material by exposing it to artificial lighting environments to check how well it retains its color.
Fastness testing uses artificial light sources like UV lamps or Xenon Arc lamps to accelerate the fading effect of sunlight over a much shorter time, allowing you to assess the resistance of the specimen quickly. Some lightfastness testers can control environmental conditions to test weathering effects.
Light Fastness Testing Methods
Primarily, the light fastness test is a type of color fastness test to check the stability of a material to color degradation under any light. There are many types of tests designed to test material fading.
- Blue Wool Scale Test
- Xenon Arc Test Chamber
- UV Light Exposure Test
- Carbon Arc Lamp Test
- Infrared Exposure Test
How Light Fastness Testing Works
Light fastness tester works using an artificial light source, this can use UV or xenon testing.
1. Sample Preparation
The samples are cut to size based on the holder frame of the xenon arc test chamber. Leneta cards are commonly used to test for paint, with a layer evenly spread on the cards.
For textile color fastness testing, mounting cards typically have a masking filter stapled on them. The filter stops the light from affecting the textile for comparison after the test.
Leneta card samples with Fanyuan Instrument labels
2. Exposure
The duration of exposure is pre-determined based on the test requirements. This can be minutes or hours to several days. Intensity and temperature are further controlled which can imitate different environmental standards.
3. Color Assessment
After the completion of the test, you can analyze the discolouration of the textile. The fading is rated on a numbered scale. The numbers identify subsequent fading runs and indicate the resistance to colour fading.
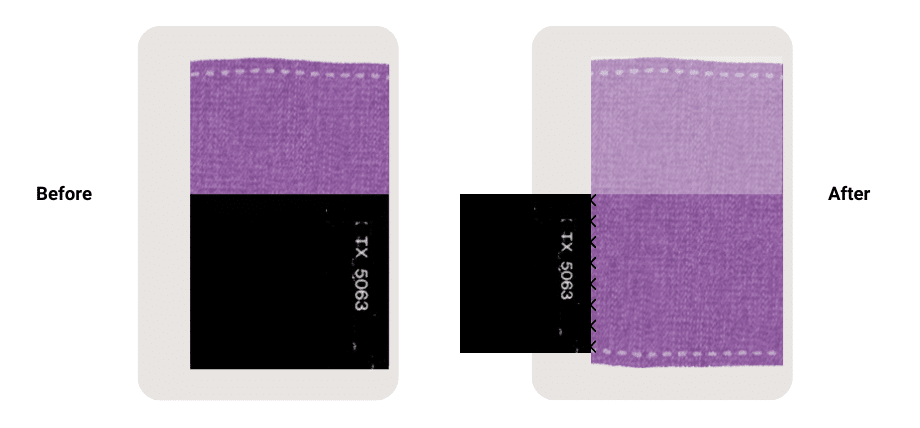

Xenon light fastness testing on textile
What Factors Influence Light Fastness
From humidity and temperature to the colour and dye itself, several factors can change the results of a light fastness test.
Chemical Composition of The Dye
There are natural and synthetic dyes popular in textile manufacturing. Almost all dyes go through a reaction called photo-degradation breaking the chemical bonds and molecular structures. Some dyes can resist sunlight better than others.
Plus, certain colours like red fade more than colours like blue.
Environment and Temperature
Temperature alters the fading rate because the photo-degradation reactions are catalyzed or sped up. Temperature control is the single biggest factor to control in your xenon arc test chambers.
Exposure Time
The way you test the light fastness of your material produces different results. Continuous tests and prolonged exposure produce a different result from an exposure with breaks even when the total exposure time are same.
Most Reliable Light Fastness Test: Xenon Arc Testing
Xenon long-arc radiation is the closest source that can stimulate natural sunlight. This makes it extremely reliable and popular for colorfastness testing. Testers like FYI Air-Cooled Xenon Arc Tester can stimulate the full spectrum making it ideal for indoor use.
This particular tester uses a long arc lamp which means your samples receive a more even distribution of light making it more suitable for testing multiple samples at the same time, bringing costs down.
Beyond sunlight, xenon long arc testing can also be used to analyze weathering effects. You can combine temperature, moisture levels, and intensity of the radiation for a controlled environment.
Standards of Colorfastness to Light
Many facilities use international standards to simplify the ratings of their light fastness tests and make their textiles acceptable for use in various conditions. There are two popular universally acceptable tests.
Blue Wool Scale
You can use the blue wool scale with eight strips dyed in different shades of blue and known resistance to fade. On this scale, 1 indicates the material fades quickly and 8 indicates the highest resistance to fading.
The specimen is attached to this scale and exposed to light in a xenon arc test chamber. The fading is compared to the blue wool and the specimen is given a rating to the closest matching blue wool.
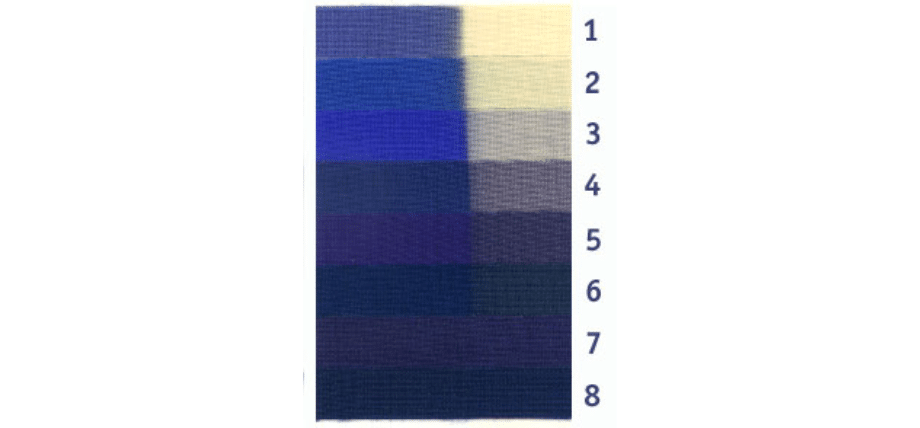

ISO 105-B02
This is an international standard with a set of steps and requirements to test the light fastness of textiles specifically. The test typically uses a xenon arc lamp to shine light on samples mounted on cards inside a test chamber. The textile’s fading level is assigned a number by comparison with the blue wool scale.
Light Fastness Testing Solutions at Your Facility | Xenon Arc Tester YG611M
ISO 105-B02 ensures consistency and reliability when assessing product colour durability. It is one of the few standards widely accepted to meet consumer expectations.
The YG611M is an air-cooled xenon arc tester specifically made for product manufacturing standards and parameters. It offers ratings in the following standards.
- ASTM G115
- ISO 105-B02
- AATCC 16.3
- JIS L0843
- GB/T 8427 and 8430
It offers complete control over temperature and weathering and can control irradiance in real time to match any standard. It has built-in technology that can continuously monitor the irradiance of xenon lamps for a stable test.
Instead of sending out samples and cuts from your textile to labs, you can make manufacturing more efficient by using affordable testing equipment and avoiding the loop of shipping samples to expensive laboratories.
Applications of Lightfastness Testing
You can use light fastness testing equipment for numerous products and many industries have already adopted this new technology.
Textile Manufacturers
From specialized gear like hiking jackets to home textiles like curtains, everything needs to be tested for quality and damage from sunlight exposure. Knowing the range of discolouration can assist with product development.
Paint Manufacturers
Paint producers require the highest standards for testing. This is because some companies produce paints specifically for canvas art which requires premium ingredients and the longest resistance to fading.
Packaging
Cardboard boxes, stickers, and plastic packaging all require color tests for brand appeal and quality marks. Customers don’t buy faded packaging even if the shelf life of your product is valid.
Key Features of Air Cooled Xenon Arc Tester YG611M
The air-cooled xenon arc tester is beneficial for your laboratory, plastic manufacturing facility, textile factory, or cosmetic lab because it has a user-friendly interface that requires no special education but a simple guide. The learning curve with this tester is among the smallest for your staff.
Apart from this, it offers
- Independent test duration for a single sample.
- Irradiance sensor that works continuously and notifies the user in real-time of unexpected changes or failure to meet standard requirements.
- In-built testing standard procedures and protocols for ISO and other universal standards.
- 15-frame specimen holding quantity at 100 x 45 mm or for larger specimens, a 7-frame capacity
- 2.5 Kw AIR-cooled xenon-arc lamp
- Window glass filters
- 150 pieces ISO standard white paper cards
Conclusion
Light fastness testing no longer has to be done at specialist laboratories and the process is now largely automated through testers.
Manufacturers can now maintain high-quality product standards and take the step towards sustainability at the same time using xenon long arc testers. With this technology, you can perform tests at your convenience and make use of quality control early on in product development.
Common Questions about light fastness testing
- What materials are typically tested for light fastness?
The most common materials for light fastness tests are clothes and textiles. The result usually is blue hues fading and lighter colors completely washing out to yellow or discolouring.
- What is the difference between light fastness and colorfastness?
Light fastness is a type of color fastness that essentially assesses the breakdown of dyes under sunlight. However, colorfastness also analyzes chemical degradation or discoloration from various chemicals.
- How many times should I test for light fastness?
Most specimens are tested for light fastness at least 3 times. There are standards like ISO which tell you the number of tests for samples.


