
Tear Strength Test and Factors Affecting It
Fabric tear test is mainly used to test the tear resistance of film, sheet, soft polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), waterproof coil, braided material, polyene warp, polyester, paper, cardboard, textiles and non-wovens.
Contents
Tear strength test method
Impact pendulum method
Suitable for woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics, etc., but not suitable for knitted fabrics, woven elastic fabrics, fabrics that may cause tear transfer and fabrics with high anisotropy.
The principle of the falling weight tearing instrument is to raise the pendulum to a certain height so that it has a certain potential energy; when the pendulum swings freely, it uses its own stored energy to tear the sample. The computer control system calculates the energy consumed when tearing the sample, thereby obtaining the force required to tear the sample.
There are two principles for fabric tear testing:
One is to detect the attenuation of potential energy and calculate the average tearing force, which can be called the “potential energy method”. It detects the angle the pendulum has turned when it swings from the initial position to the highest position on the other side through a pointer or encoder that can maintain the maximum swing. Calculate the difference in height of the pendulum’s center of gravity to determine the amount of potential energy decay of the pendulum. Mechanical tearing instruments and electronic (mathematical) tearing instruments using encoders belong to the potential energy method.
The second is to detect the attenuation of kinetic energy and calculate the average tearing force, which is called the “kinetic energy method”. It is equipped with a photoelectric or other angular velocity detection device to detect the difference in angular velocity of the pendulum at a certain position when the sample is not clamped and when the sample is clamped, and the attenuation of the kinetic energy of the pendulum is calculated.
Test method: The weight falls due to gravity and then suddenly applies a force to the sample, thereby tearing the sample.
Pants method
This method is suitable for woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics, etc., but not suitable for knitted fabrics, woven elastic fabrics, fabrics that may cause tear transfer and fabrics with high anisotropy.
After cutting the sample to the specified size, clamp the two legs of the trouser-shaped sample so that the cut line of the sample is a straight line between the two clamps. Turn on the instrument, apply tensile force in the direction of the incision, and record the tearing strength until the tear reaches the specified length. Calculate the average value of the highest and lowest peaks in the specified area, and measure the tearing strength.
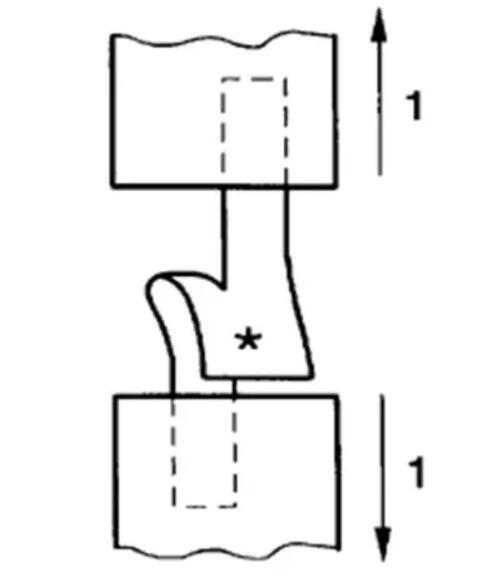
Test method: Constant speed stretching: stretching speed 100mm/min, gauge length 100mm.
Trapezoidal method
Both woven and nonwoven materials can be tested for tear strength using the trapezoidal method.
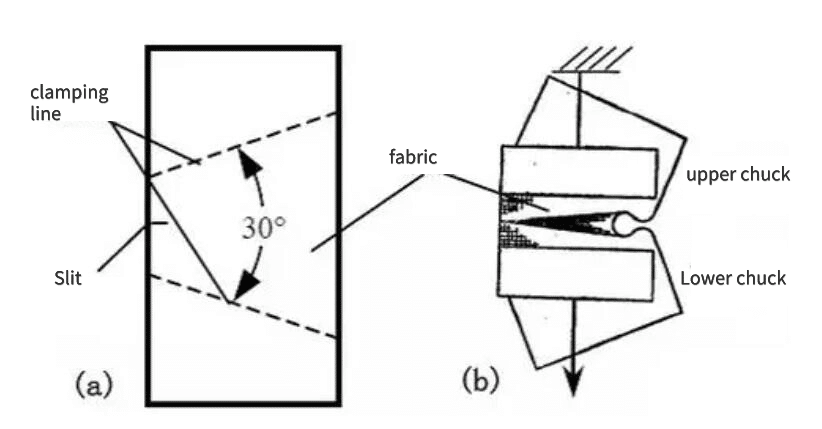
Draw a trapezoid on the sample and cut a notch on the short side of the trapezoid. Use the clamps of the strength tester to clamp the two non-parallel sides of the trapezoid so that the notch is located in the middle of the two clamps. Apply continuously increasing force to the sample to cause the tear to propagate along the width of the sample, and determine the average maximum tearing force.
Test method: Constant speed stretching: stretching speed 100mm/min, gauge length 25mm.
Among these three tear strength testing methods, the impact pendulum method and the trouser-shaped method have certain limitations in the sample requirements. The trapezoidal method has a wider application range and can obtain better test results. However, the principles and testing methods of these three methods are different. When choosing a specific method, you should choose according to the relevant textile standards and specific needs.
Elmendorf tearing tester
The Elmendorf Tear Strength Tester is an instrument specially used to test the tear strength (strength) of fabrics. It uses the impact pendulum method to measure tear strength, also known as the pendulum or falling weight tear strength tester. There are manual electronic tear strength testers, digital Elmendorf tear strength testers, etc.
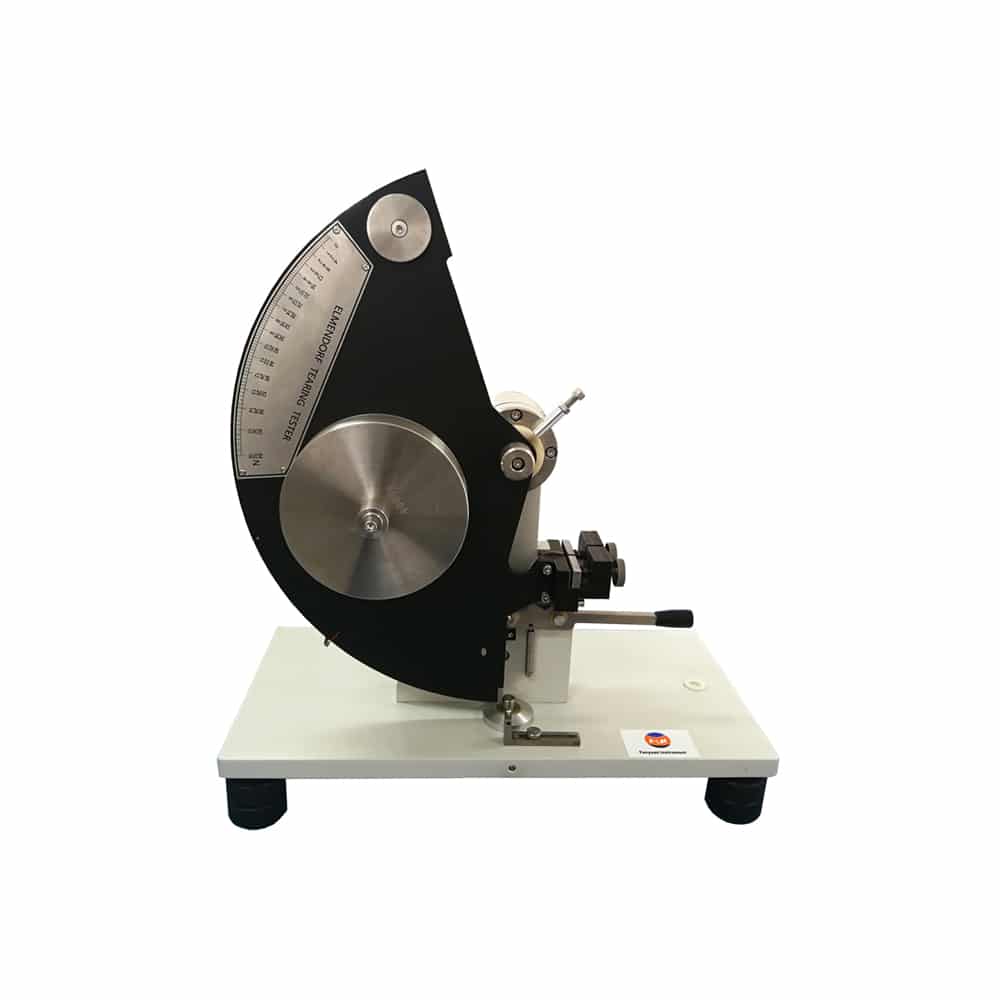
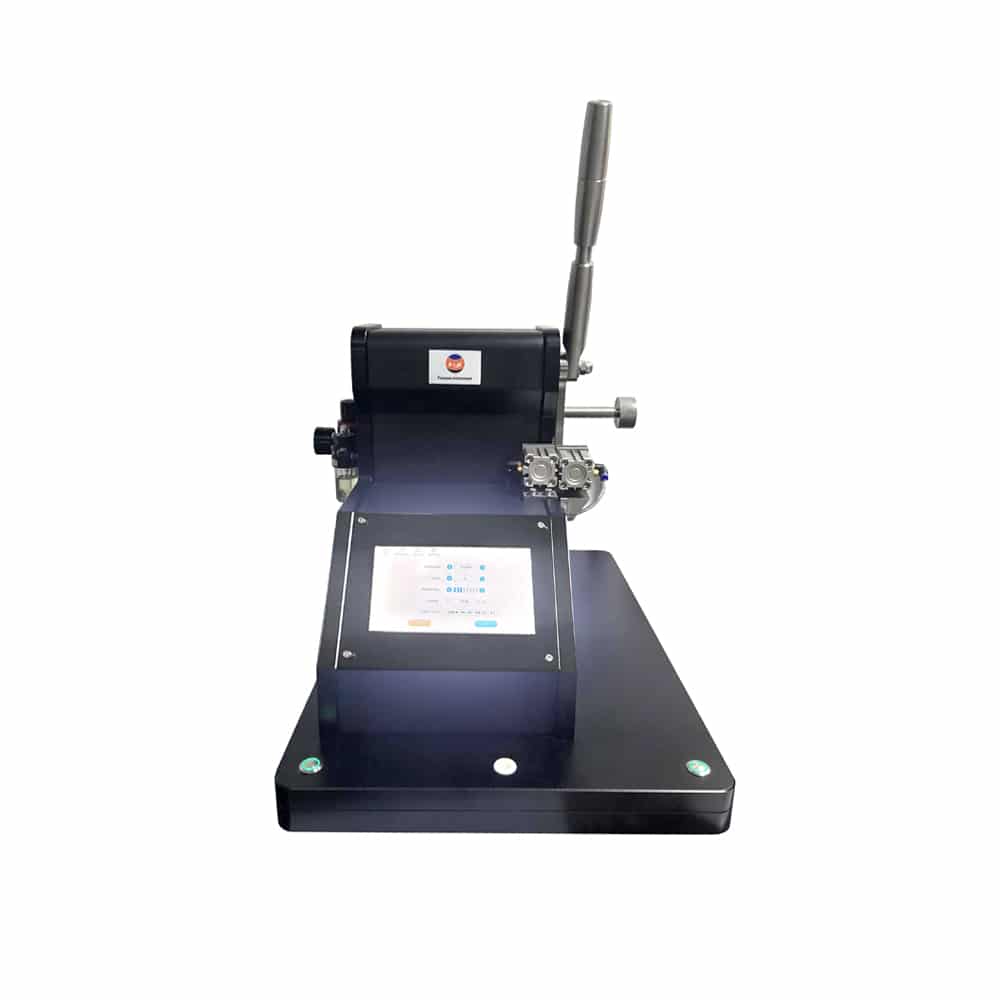


This instrument is widely used in the production of peel-off to finishing products for durability. For example, for fabrics finished with resin, additives or paint, the deformation ability of the yarn is reduced, and the tear strength can better reflect the changes in the fastness of the textile after finishing than the tensile breaking strength. Many industrial fabrics also regard tear strength as one of the important items for product quality inspection. The tear properties of a fabric are very important to the durability of the fabric.
Factors affecting tearing strength
Raw materials
Different raw materials have obvious differences in their resistance to external tearing and tensile forces.
Yarn properties
Thread density: thicker yarns have better tear resistance and tensile strength.
Filament/Short Filament: Filament can be directly turned into yarn for textile use, while short fiber needs to be twisted to gather the short fiber into yarn, so the strength of short fiber is lower than that of filament.
Twist: Twist can make short fiber yarns or filaments better hold together, form cohesion, improve strength and elasticity, thereby improving the tearing strength of the fabric. However, the twist also has a certain limit value. An excessively high twist not only fails to improve the strength and elasticity, but also makes the yarn brittle, which will reduce the strength and elasticity.
Elongation at break: The tearing strength of the fabric is approximately proportional to the breaking strength of the yarn and closely related to the elongation at break of the yarn. When the elongation at break of the yarn is large, there are many yarns in the stress triangle area that bear the tearing strength at the same time, so the tearing strength of the fabric is large.
Fabric structure
Plain weave<twill weave<satin weave
Density
As the fabric density increases, the tear resistance increases. The most critical factor is that the organization and density affect the tearing strength by affecting the slipability of the yarn.
Post-finishing processing technology
The sanding process polishes the surface of the fabric to produce short and neat small villi on the surface of the tissue. In this way, the yarn structure on the surface of the fabric is destroyed, and the yarn strength is reduced.
Coating: Apply a layer of chemical slurry on the surface of the fabric to make the surface of the fabric have various functions (such as anti-velvet, waterproof). This type of process slurry will fix the warp and weft yarns of the fabric in relative positions and cannot move. This results in a significant reduction in the tear triangle area of the fabric. Therefore, the strength after coating will be significantly lower than that before coating, and tearing must be assessed when doing similar processes.
Comments are closed.


From the engaging storytelling to the insightful analysis, this blog truly stands out.
From the captivating storytelling to the insightful analysis, this blog delves deep into various topics.
Want to delve deeper into the topics discussed? This blog provides ample opportunities for further exploration and learning.
I join the chorus of praise for this exceptional blog, which never fails to impress with its thoughtfulness and depth.