Mastering Material Testing: The Essential Guide to Coefficient of Friction
The coefficient of friction tester is a measuring instrument used to measure the static and dynamic friction coefficients of materials such as plastic films and sheets, rubber, paper, cardboard, woven bags, fabric styles, metal composite belts for communication cables and optical cables, conveyor belts, wood, coatings, brake pads, wipers, shoe materials, tires, etc. when sliding. By measuring the smoothness of materials, the production quality and process indicators of materials can be controlled and adjusted to meet the requirements of product use. In addition, it can also be used for measuring the smoothness performance of daily chemical products such as cosmetics and eye drops.
Contents
Related definition
Antistatic: Property of a material that reduces its propensity to acquire electrostatic charges or allows electrostatic charges to dissipate quickly.
Conductive: Providing a sufficiently high conductivity so that potential differences over any parts of a material or object are not sufficiently large to be of practical significance.
Note: In general, a conductive material has a resistance below about 105 Ω, but different standards may define different resistance ranges for this term.
Frictional charge density: Quantity of charge per unit area on a fabric specimen generated by friction between the specimen and other fabrics.
Electronic charge: The charge carried by the specimen after friction with the standard cloth for a certain period of time.
Note: For non durable anti-static textiles, the pre washing charge should not exceed 0.6 μC per piece; For durable anti-static textiles, the charge before and after washing should not exceed 0.6 μC per piece.
Test method of coefficient of friction
The methods for measuring the coefficient of friction are manual friction and electric charge. The second method is easier to operate, so we will provide a detailed introduction to the electric method in the following.
Principle
Electric charge: Simulate the frictional charging of the specimen using a friction device, and then put the specimen into a Faraday pail to measure its charged charge.
Test equipment
Faraday pail (As FIG.1 shows)
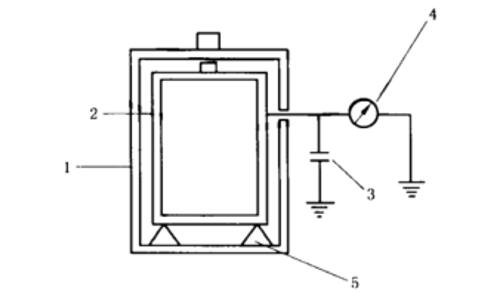
1. Outside pail
3. Capacitor
5. Insulating bracket
2. Inner pail
4. Electrostatic voltmeter
Friction charged drum testing device (As FIG.2 shows)
- The inner surface of the drum and the inner surface of the lid are covered with standard cloth.
- The testing device should meet the following conditions:
- Drum inner diameter: not less than 460mm;
- Drum depth: more than 350mm;
- Drum diameter: more than 280mm:
- Drum speed: (50 ± 10) r/min;
- Number of drum blades: 3 pieces;
- Temperature inside the drum: (60 ± 10) ℃. Heating is achieved through electrical heating and air conditioning;
- Exhaust volume: above 2m3/min.
- Friction material for the drum lining: Nylon standard cloth. The device should also be wrapped around the injection port.
- Electrostatic voltmeter: Accuracy of 1 ± 1%, input resistance of 1×1012 Ω or more.
- Capacitor: The capacitance value should match the range of the electrostatic voltmeter, and the insulation resistance should be above 1012 Ω.
- Insulation bracket: polytetrafluoroethylene with insulation resistance above 1012 Ω.
- Insulating tape: insulation resistance above 1012 Ω.
Note: Other materials may be used for friction materials as needed or after consultation and agreement among relevant parties.
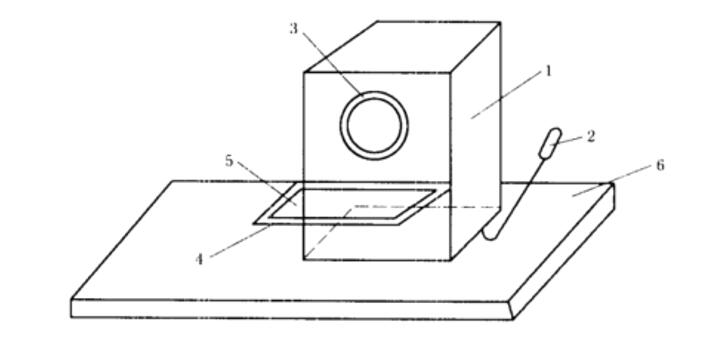
1. Drum
3. Insulating tape
5. Standard cloth
2. Handle
4. lid
6. Base
Test environment
The environmental conditions for humidity control and testing atmosphere are: temperature (20 ± 2) ℃, relative humidity (35 ± 5)%, and ambient wind speed should be below 0.1m/s.
If tests are carried out under the conditions of other temperature and humidity, that effect shall be mentioned in the test report.
Prepare for sample
Preprocessing
- If necessary, wash according to the 7A procedure in GB/T8629-2001. Depending on the sample wearing conditions or as agreed by relevant parties, wash 5, 10, 30, 50, 100, etc. can be selected. When washing multiple times, the time can be accumulated for continuous washing. Or wash according to the method and frequency recognized by the relevant parties.
Note: When accumulating time, wash the 7A program, and accumulate the time for washing 1, washing 2, and washing 3 separately.
- Pre dry the sample or wash sample at 50 ℃ for a certain period of time.
- The pre dried sample should reach moisture balance in the testing environment without contaminating the sample.
Sample
Take at least one product as a sample for each sample.
Test steps
- Turn on the friction device to reach a temperature of (60 ± 10) ℃.
- Place the sample in a simulated wearing state (buttoned or zipped) into the friction device and run for 15 minutes.
- After the operation is completed, remove the sample from the friction device (insulated gloves must be worn to remove the sample) and put it into the Faraday pail. During the operation, the sample should be at least 300mm away from objects outside the Faraday pail.
- Measure the electrical charge of the sample using a Faraday pail.
- Repeat the operation 5 times. Allow it to stand for 10 minutes between each time, and use a power dissipation device to remove electricity from the sample and the standard cloth inside the pail.
- For products with lining, the lining should be flipped outward and the above testing steps should be repeated again. Record the results in the report.
Test result
Take the average of 5 measurements as the test result and round it to 0.1.
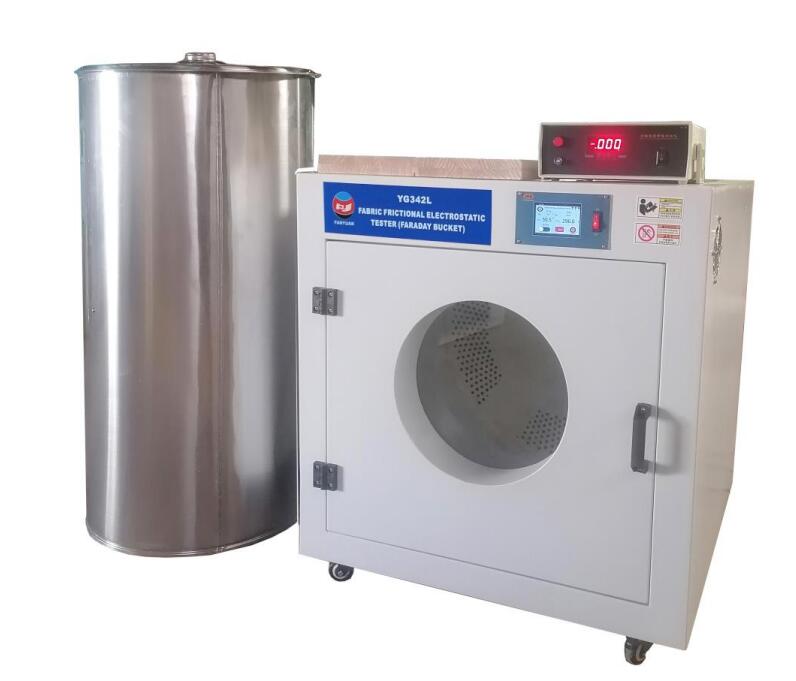
Coefficient of friction tester
Our product — YG342L Fabric Frictional Electric Charge Tester can not only use this method, but also use the manual friction method. It is used for measuring the charge quantity of fabrics and clothing charged by friction under laboratory conditions.



