
The knitting principle of small knitting machine
Small knitting machine is also known as dyeing test knitting machine. The previous article introduced the definition of the dyeing test knitting machine. And here I will tell you the knitting principle of small knitting machine.
Contents
The internal structure of knitting part in small knitting machine
Knitting needles
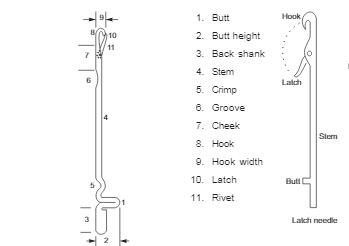
The top hook and the latch needle form the knitting needles. Latch needles are given sliding movements in individual grooves called tricks of the cylinder. The latch swing freely and the stem is a straight portion with a protruding butt. Through the butt the reciprocating movement to the needles is given. in addition,the latch needles are self acting, and requires only previous loop on the stem and do not require any outside agency to close the hook. The swinging latch has a cup at its end and is riveted to the stem.
Sinkers
Sinker is a thin metal plate with action at right angles to and fro between adjoining needles. And it may perform one or more of the following functions:
- Loop formation
- Holding down
- Knocking over
The main object of a sinker is to assist the needles in loop formation by sinking or knitting the newly laid yarns into a loop. As its forward edges of catch advantages between the two adjoining needles.
It also holds down the loops at a lower level of the needle stems and prevents the old loops from being lifted as the needles raise to clear them for their hooks.
The third function is a knocking over at which the needle passes through the old loop by drawing a new loop.
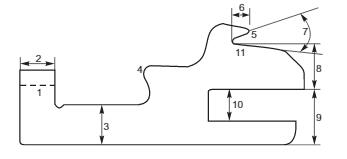
1.Butt 2.Butt breadth 3.Height of shank 4.Buldge 5.Neb 6.Length of Neb 7.Throat Angle
8.Sinker Platform Height 9.Breadth of Lower Shank 10.Clearance 11.Throat
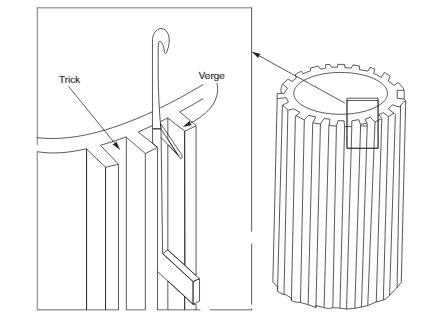
Cylinder in small knitting machine
The cylinder is a steel circular bed . There are grooves/tricks/notches on the outside where we can mount the needle .With reference to the tricks, the needles move vertically up and down by their butt being in contact with the cam track. At the same time,the number of needles per inch decides the gauge of the machine.
The knitting principle of small knitting machine
The knitting principle usually has five steps. They are Run-in, Clearing, Feeding, Knock over, Loop pulling.
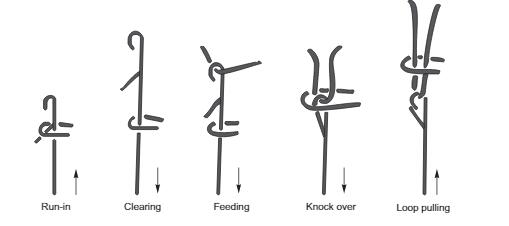
Run-in
In the running position, the held old loop rests on the top of the open latch. The held loop is positioned in the throat of the sinker when the sinker moves forward and the needle moves upward for clearing. The held loop is held by the throat and hence its movement along the needle is restricted.
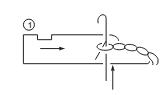
Clearing
Clearing occurs as the held loop slips of the latch and on to the stem as the needle moves upwards. The sinker remains at its forward position when the needle attains its clearing position.
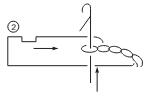
Feeding
A downward movement enables the needle hook to engage a new piece of yarn. This is feeding step. The sinker retracts when the needle comes down after feeding. At this stage, due to sinkers retraction, fabric or held loop is eased out. Also the sinker belly supported the fabric or held loop and hence its movements along the needle is prevented.
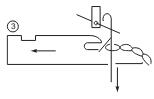
Knock over
As the needles continue downwards .Under the influence of the held loop,the latch turns to close. Knock over occurs as the help loop disengages from the needle. Then sinker remains in backward position and the needle descends to its lowest position drawing the new loop through the old one.
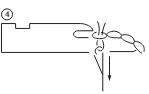
Loop pulling
After knock over, the loop pulling step begins to form a new knit loop. The needle must return now to the running position to complete the cycle. Before the needle ascends, the sinker moves forward to push the knitted fabric a little and to hold the old loop away from the head of the needle and to be in a position to control the fabric.
If you need more information about small knitting machine. Or the price of dyeing test knitting machine, please send email to [email protected].
Comments are closed.



Really helpful blog. Hope your next article!
Thanks for your comment!