
Martindale Abrasion Tester Working Principle and Standards
The Martindale abrasion tester (Martindale method) is used to test the abrasion resistance and apparent pilling properties of woven fabrics, knitted fabrics, non-woven fabrics, decorative materials, coated fabrics, etc.
Working principle
The fabric to be tested is mounted in the upper specimen fixture and rubbed against the abrasive material mounted on the grinding table. The friction trajectory is a Lissajous figure (an important feature of the Martindale method). After the specified friction stage according to the test requirements, remove the fabric and calculate the wear resistance index or use visual description to evaluate the fuzzing and pilling levels of the sample.
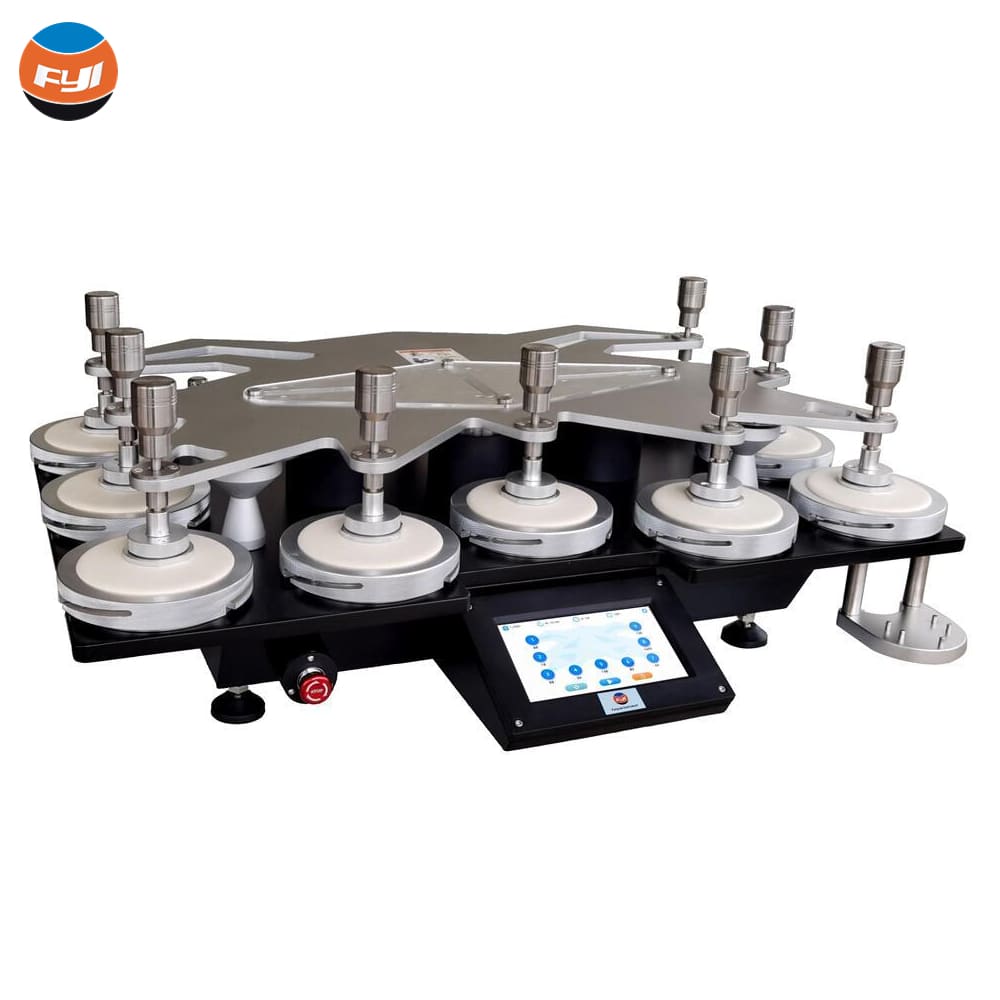
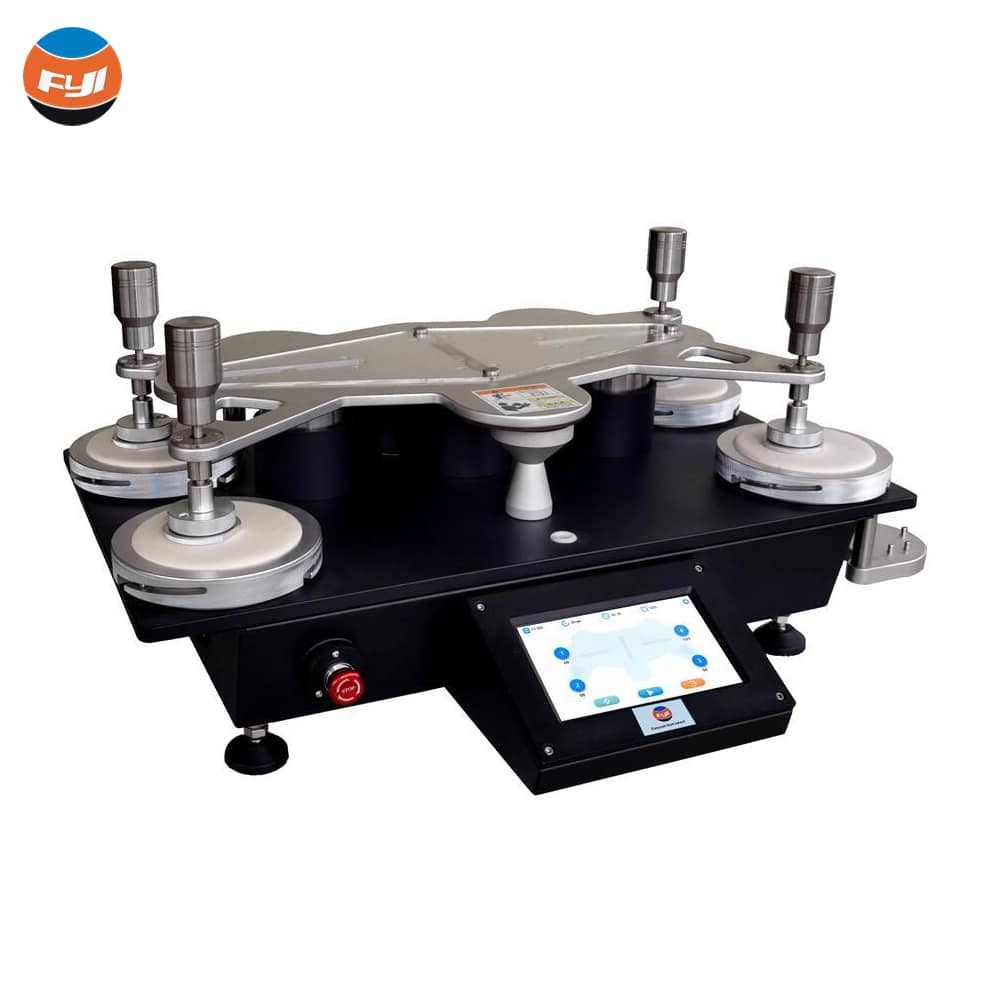


Operation method
1. Sample preparation
In a standard environment, lay it flat and without stretching for a period of time according to different standards. Such as 24h (GB/T 4802.2-1997), 16h (EN ISO 12947-4:1998)
2. Selection of specimens
Cut a sample from different parts of the entire door fabric, and the sample must be representative. If it is a fancy fabric, the sample should include all different textures and colors presented on the cloth surface;
3. Remove the load and load shaft from the testing machine;
4. Remove the top plate and test fixture;
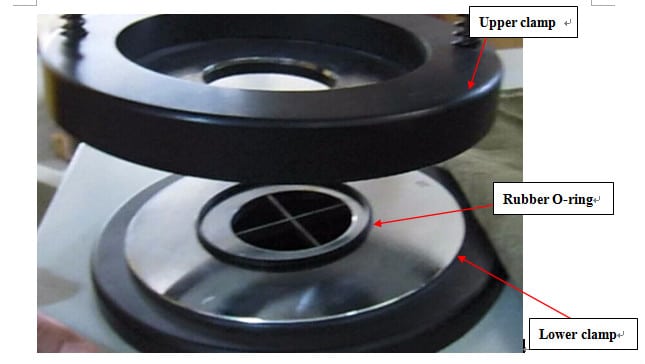
5. Sample device
Loosen the fixing ring on the test fixture, take off the sample pressing piece, and place the sample into the base of the test fixture. When the fabric being tested is not larger than 500 g/m2, a piece of polyester foam should be placed between the sample and the metal plug of the sample clamp; if the fabric is larger than 500 g/m2, or it is a composite fabric, there is no need to put a piece of polyester foam. The specimens on each specimen clamp should be subjected to the same tension.
6. Wool felt and friction cloth device
Place the felt and abrasive on the grinding table, place the weight on the abrasive, then put on the pressure ring and tighten the nut so that the pressure ring fixes the abrasive on the grinding table.
7. Place the grinding head on the abrasive and apply pressure;
8. Place the test fixture containing the sample face down on the base fixture, adjust the circular groove of the test fixture to align with the load shaft, so that the load shaft is inserted into the circular groove of the test fixture;
9. Set the number of times according to the standard, turn on the switch, start the test, and automatically stop after reaching the set number of times;
10. Remove the sample and compare it with the standard sample in the rating box.
Martindale Abrasion Tester Standard Comparison
International standards
ISO12947.2-1998 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics by Martindale method – Part 2: Determination of specimen damage”;
ISO12947.3-1998 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics using the Martindale method – Part 3: Determination of mass loss”;
ISO12947-4—1998 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics using the Martindale method – Part 4: Assessment of changes in appearance”.
American Society for Materials (ASTM) standards
ASTMD4966-2010 “Martindale Abrasion Resistance Tester for Fabric Abrasion Resistance Testing”.
EU standards
ENISO12947-2:1998 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of Martindale fabrics – Part 2: Determination of specimen damage”;
ENISO12947-3:1998 “Textiles – Determination of the abrasion resistance of fabrics by the Martindale method – Part 3: Determination of mass loss”;
ENISO12947-4:1998 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics by the Martindale method – Part 4: Assessment of changes in appearance”.
German Institute for Standardization (DIN) standards
DINEN ISO12947-2-2007 “Textiles. Determination of fiber abrasion resistance by Martindale method. Part 2: Test damage determination”;
DINEN ISO12947-3-2007 “Textiles. Determination of fiber abrasion resistance by Martindale method. Part 3: Determination of mass loss”;
DINEN ISO12947-7-2007 “Textiles. Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics by Martindale method. Part 4: Assessment of appearance changes”.
British Standards Institution (BS) standards
BS ISO12947.2-1998 “Textiles – Determination of fabric abrasion resistance by Martindale method – Part 2: Determination of sample damage”;
BS ISO12947.3-1998 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics by Martindale method – Part 3: Determination of quality loss”;
BSEN ISO12947-4-1999 “Determination of abrasion resistance of textile fabrics by the Martindale method – Part 4 Assessment of appearance changes”.
Chinese national standards
GB/T21196.2-2007 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of Martindale fabrics – Part 2: Determination of specimen damage”;
GB/T21196.3-2007 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics by Martindale method – Part 3: Determination of quality loss”;
GB/T21196.4-2007 “Textiles – Determination of abrasion resistance of fabrics using the Martindale method – Part 4: Assessment of appearance changes”.
The standards given above are the Martindale method standards for fabric abrasion resistance testing issued by several influential international standardization organizations. Among them, EU standards, German Standards Institute standards and British Standards Institute standards are all equivalent to the International Organization for Standardization standards. The Chinese national standard has been revised to adopt the International Organization for Standardization standard. The detection method is basically the same as the International Organization for Standardization standard. Only the scope of application of the standard has added coated fabrics, and for the detection of coated fabrics, corresponding provisions for damage and friction of coated fabrics have been added. Load parameters, standard abrasives, and standard abrasive replacement requirements. American Society for Materials standard ASTM D4966-2010 “Testing of Fabric Abrasion Resistance with Martindale Abrasion Resistance Tester” includes two parts: provisions on abrasion resistance testing methods, Martindale abrasion resistance testers and auxiliary materials. The testing methods are in line with international standards. The standards of the Organization for Standardization ISO12947.2~4 are basically the same. They are slightly different from the standards of the International Organization for Standardization ISO12947.3~4 in terms of the measurement of mass loss and the assessment of appearance changes. The end-point conditions of the test and the expression of the test results are more simplified.
There are three methods for measuring the abrasion resistance of fabrics using the Martindale method: sample breakage measurement, mass loss measurement and appearance quality change method. Among the three methods, the commonly used method is to measure sample damage. This method has small errors, the test results are intuitive and clear, and the wear resistance of different fabrics is easy to compare. It is commonly used in clothing products and decorative fabrics. The expression form of the test results of the mass loss measurement method and the appearance quality change method is relatively complex, but it can reflect the wear resistance of the sample at different friction stages. It has strong practicality in analyzing the uses of fabrics in production enterprises or scientific research institutions.
Comments are closed.


Both informative and entertaining, this article strikes the perfect balance between education and engagement.
Join me in applauding the author’s ability to convey their ideas concisely and eloquently.
Many blogs lack substance, but this one is a breath of fresh air with its well-researched articles.