Cotton spinning system and process
How to process the disorganized and horizontally closely connected fibers into vertical order and smooth yarn with certain requirements, it is necessary to turn the block fiber into a single fiber state, completely remove the horizontal connection of the fiber raw materials, and establish a strong longitudinal connection between the end and the end. The former is called the loosening of fibers, and the latter is called the collection of fibers. Cotton spinning is the process of using certain systems, processes, equipment and technology to loosen and assemble textile staple fibers into yarns that meet certain requirements.
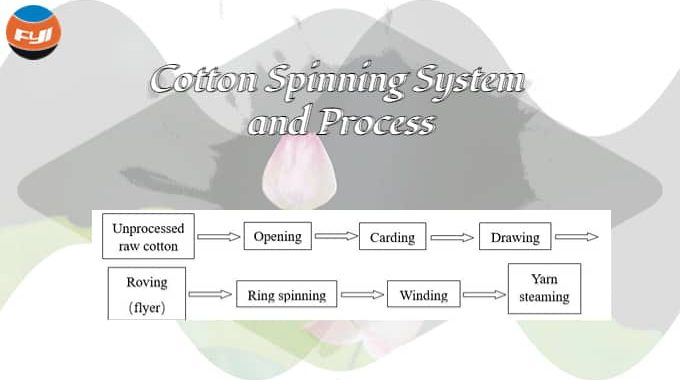
The process of cotton spinning system generally includes raw material preparation, opening, carding, impurity removal, mixing, drawing, merging, twisting and winding. The following is the process description and application.
Unprocessed raw cotton——Opening——Carding——Drawing——Roving(flyer)——Ring spinning——Winding——Yarn steaming
Ginning
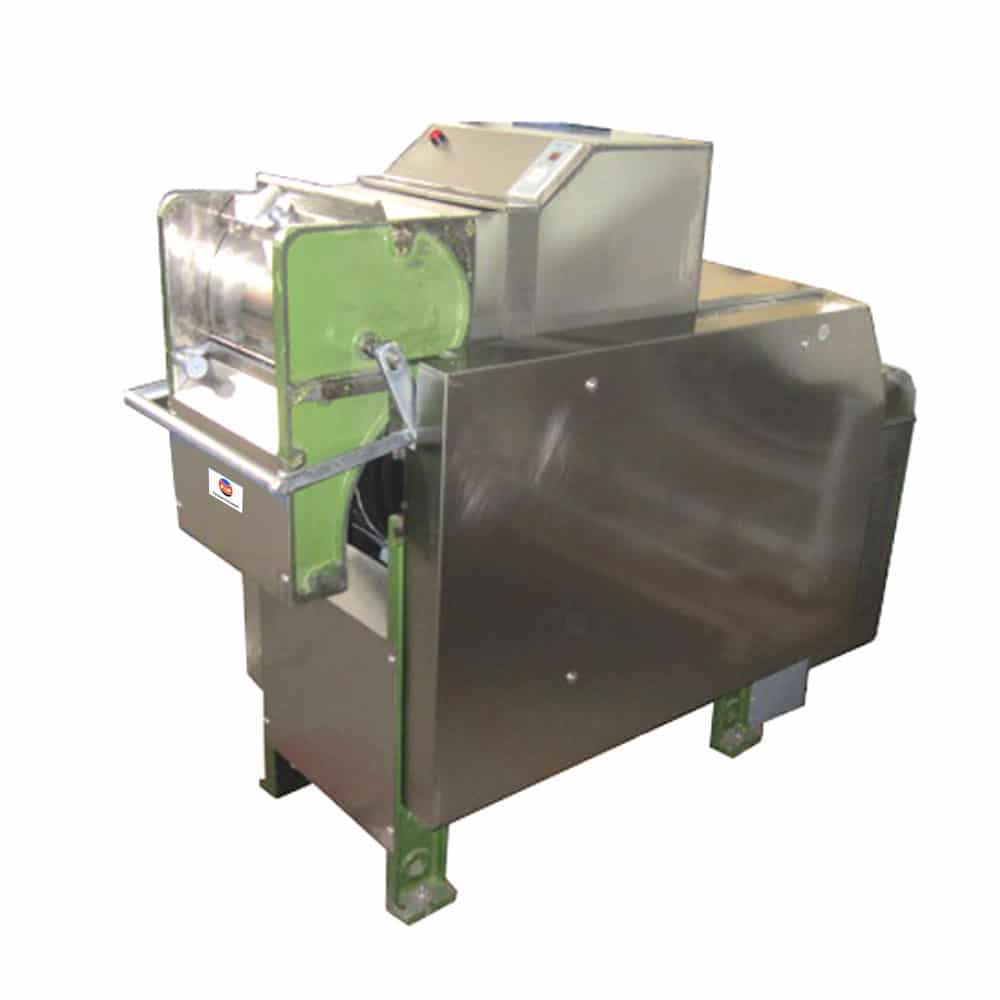

Cotton ginning is the process of separating cotton seed from the lint so that the lint will be baled and goes to textile industries for further processing whereas the cotton seed is milled by oil mills to produce edible oil. It’s the first step of cotton spinning process.
Opening
An opening machine for separating the fibres from intermingled impurities in cotton tufts.
Opening machine comprise a supply cotton plate onto which the cotton tufts to be processed are introduced. At the bottom of the plate there is a licker-in which cooperates with cleaning blades to split up the fluffy masses of cotton at least partially into their individual constituent fibres. Therefrom, eliminating the intermingled vegetable impurities (parts of leaves, of capsules, of seeds, earth, etc.). In the vicinity of the licker-in there are usually suction openings for removing the impurities separated from the fibres and a duct through which the impurity-free fibres are removed.
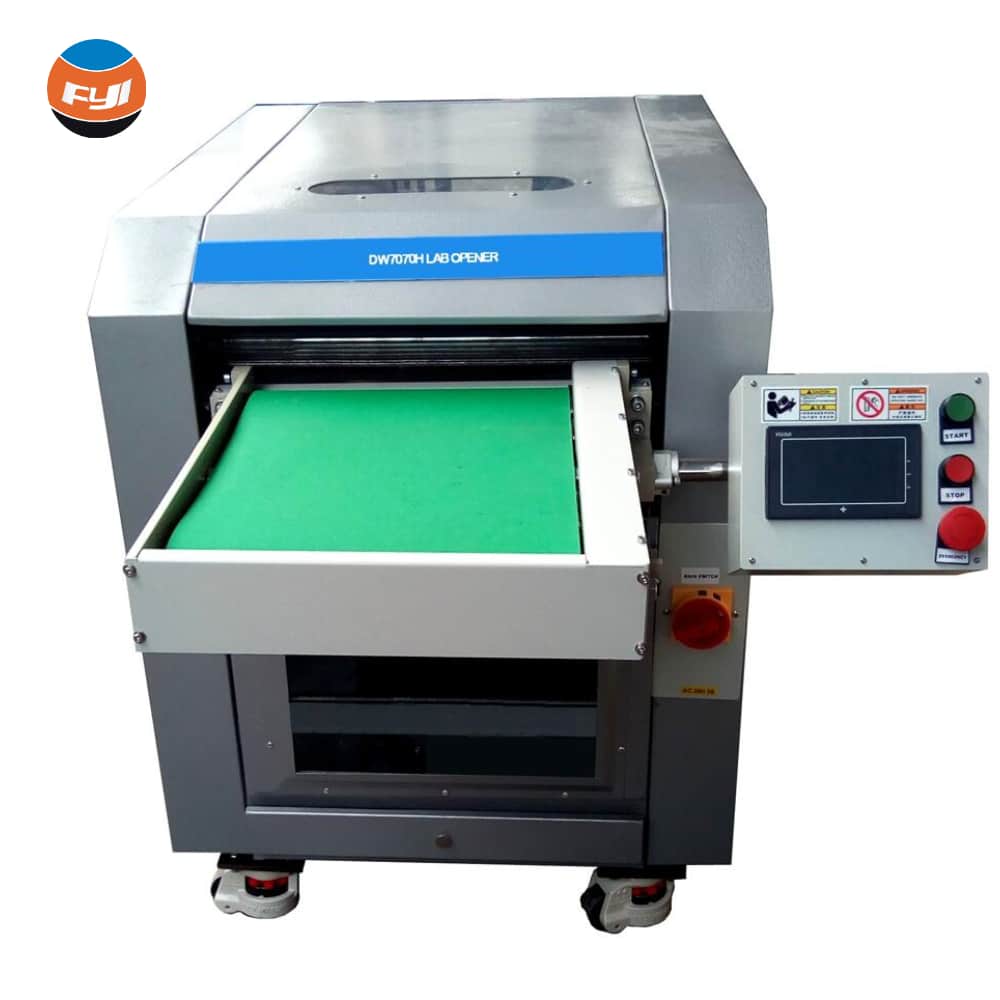

Carding

In the Carding machine, the fibrous material is worked into a belt of untwisted fibres in the form of a web that will be condensed into carding sliver and passed on to subsequence processing stages.
The purpose of the carding operation is to turn raw material consisting of tufts of fibres, which have already undergone certain initial cleaning and opening processes, into a belt of untwisted fibres in the form of a web that is, as far as possible, free of impurities and non-homogeneities such as residual dirt from the previous process, waste and tangles or “neps”.
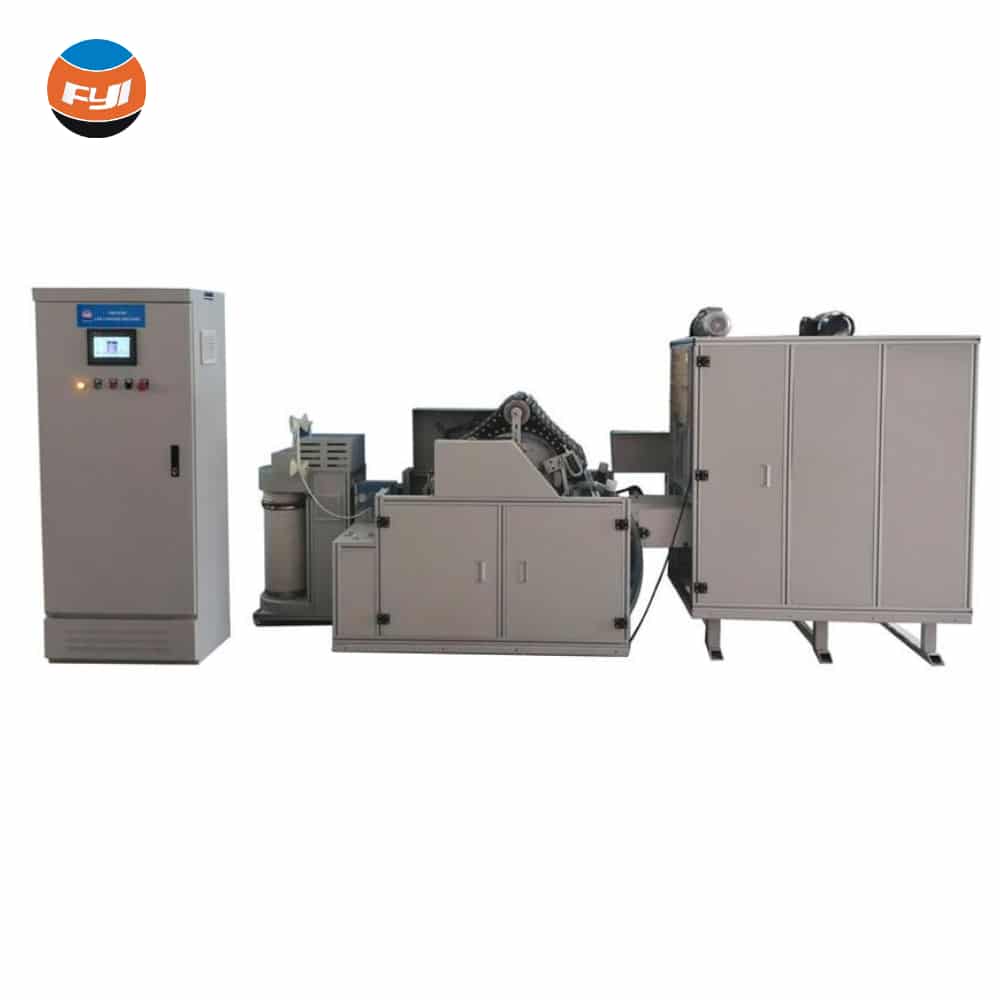
Drawing
Drawing frames are mainly used to produce a fiber fleece that is as uniform as possible from a multiple number of fiber slivers. For this purpose, the stretch has one or more stretching units, which in turn comprise series of drawing elements, typically in the form of several successively arranged pairs of rollers, whereas the fiber slivers are guided between the respective pairs of rollers by clamping. Since the pairs of rollers feature peripheral speeds that vary and increase in the running direction of the sliver, the fiber slivers are finally stretched and thereby made uniform.
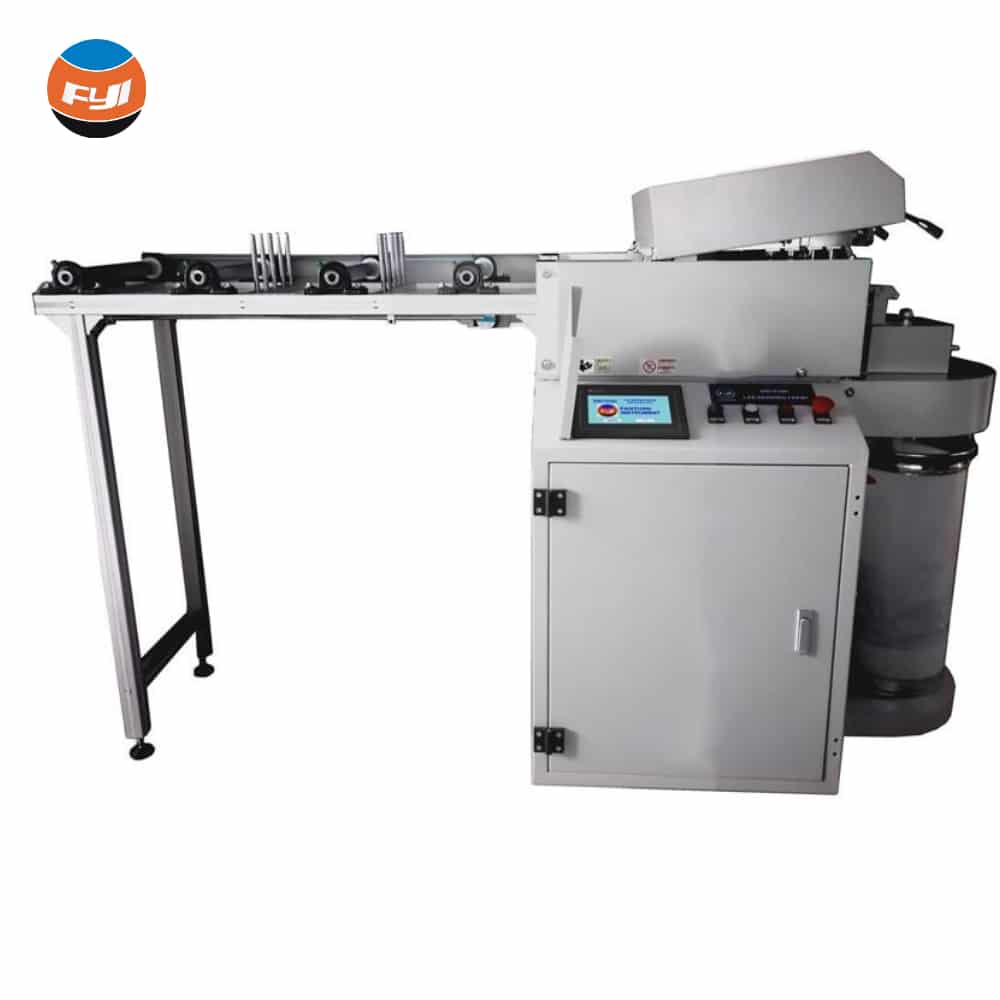

Roving
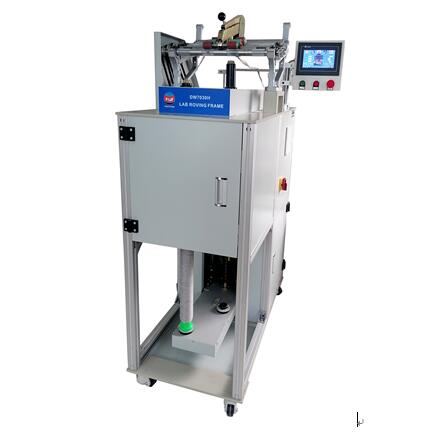

In a roving frame, also called roving machine or fly frame, a roving is produced from a sliver. The sliver is produced upstream of the yarn production process in a draw frame. The roving is the starting product for produce a yarn e.g. in a ring spinning machine. Thus, the roving is significantly thicker than a yarn but also significantly thinner than a sliver.
The main task of roving of a roving frame is to further draft a sliver into a fibre strand of finer count, the so called roving. This intermediate production step is necessary as the ring spinning machine is not capable of processing a thick sliver to a yarn of fine count. Moreover, the handling of a sliver in a ring spinning machine is still unsolved. This, because there is not enough space in the ring spinning machine for storing the bulky sliver cans in which the sliver is provide due to the poor strength of the sliver.
Additionally, the roving frame’s job is to add a protective twist to the roving so as to increase the strength of the textile fiber strand and make it transportable without being damaged. Without a protective twist, neither the sliver nor the fine count roving made from the sliver has much coherence.
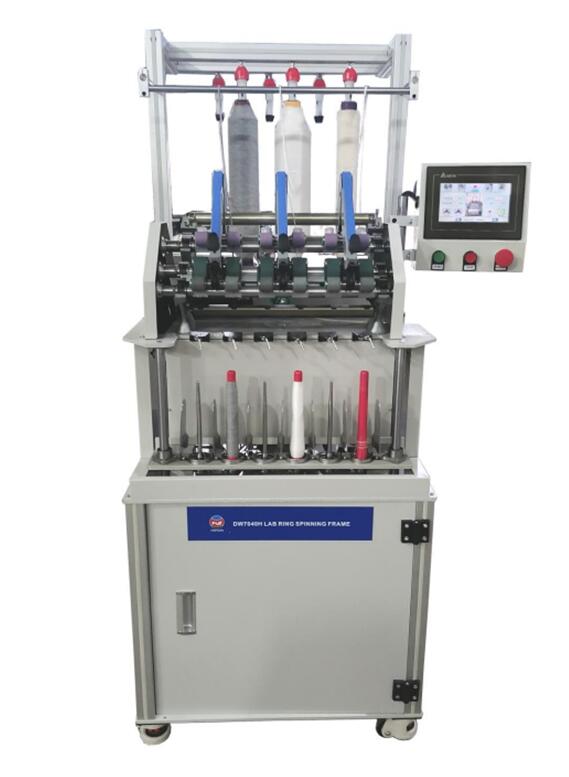
Ring spinning
Ring spinning is essentially the process in which a roving of textile fibres is transformed into a twisted yarn by first performing a drafting and controlled elongation of the roving by which it is given the desired dimensions, which determines the yarn count of the yarn produced from it, and then giving the bundle of fibres of the roving, which have received only a slight twist in the preceding working and are still substantially parallel, an effective and necessary twist to give the yarn an adequate strength by making it pass along a path in high speed rotation between a fixed ring and a rotating spindle with the interposition of a ring driven by the spindle itself. The yarn thus twisted is collected by winding it on a bobbin, carried by the spindle, to form a spool which, when completed, is transferred for subsequent operation.

Winding
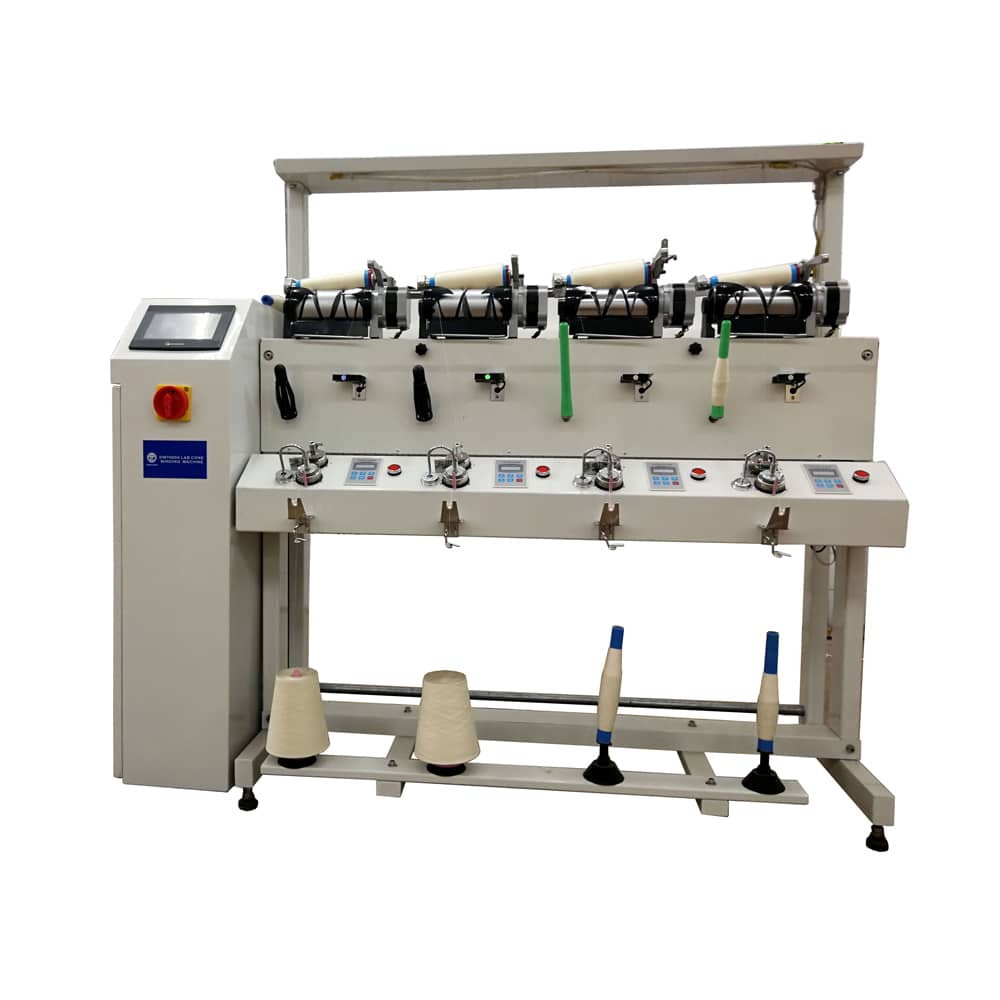

Winding machine includes a yarn supplying section, a yarn accumulating device, a tension applying section, a yarn joining device, and a package forming section. The yarn supplying section supports a yarn supplying bobbin with a yarn wound thereon. The yarn accumulating device winds and accumulates the yarn from the yarn supplying bobbin supported by the yarn supplying section. The tension applying section applies tension on the yarn being wound by the yarn accumulating device. The yarn joining device joins the yarn from the yarn supplying bobbin caught by the supplied yarn catching section and the yarn that is wound in the yarn accumulating device. The package forming section pulls the yarn from the yarn accumulating device and winds the pulled yarn to form a package.
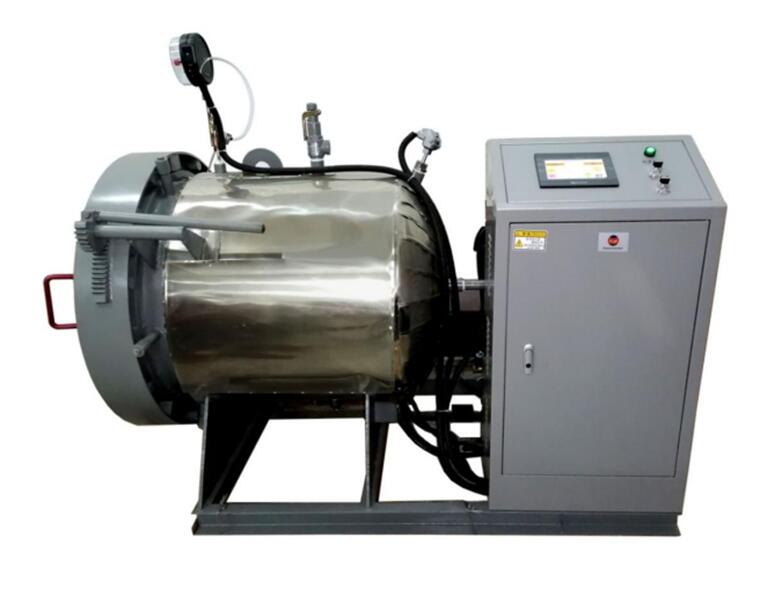
Yarn steaming
Yarn is steamed (heat set) in an autoclave after spinning so as to reduce or eliminate the twist liveliness (torque) and snarling tendency of the yarn and thereby facilitate the subsequent winding and twisting (folding) of the yarn and to avoid fabric distortion.

Comments are closed.



When it comes to covering diverse topics, your blog is a go-to resource for reliable information.
How you manage to consistently publish high-quality blog posts is truly commendable.
Need a reliable source of information? Look no further – this article has got you covered.