
Guide to Crease Recovery
The crease recovery property of fabric is one of the important indexes to evaluate the properties of fabric. Measuring the crease recovery Angle of folded fabric samples by instrument is a common method to measure the crease recovery property of fabric.
Contents
Crease recovery properties of fabrics
When the fabric is used and stored in the process, due to folding, bending arch, compression, washing and other external forces to produce local deformation, the formation of creases or wrinkles. Even after the external force is removed, it fails to return to the original flat state, which is called creasing. Creases seriously affect the appearance of the fabric, and the wear of the fabric is often produced along the direction of creasing, accelerating the damage of the fabric. It is of great significance to understand the crease bending and recovery process of fabric and its mechanism to test the crease recovery performance of fabric.
Generally, the formation of fabric creases can be divided into two stages: fabric creasing under the action of external force and fabric creasing recovery after the removal of external force. Crease generation: Under the action of external force, the fabric bends and deforms, because the external force is much greater than the resistance of the fabric due to bending. Therefore, the fabric is forced to bend and deform, that is, beyond the flexural elastic deformation range of the fabric, resulting in yield deformation. This deformation includes the slip dislocation between the warp and weft yarn lines of the fabric, the slip between the yarn fibers, and the stretching deformation of the fibers under the action of external forces. When the fabric reaches a certain deformation, the internal stress of the fabric weakens with the extension of the external force acting time, that is, the stress relaxation occurs. Therefore, whether the fabric produces creases depends on the shape variable of the fabric and the relaxation state of the internal stress of the fabric.
Crease recovery: After the external force is removed, the fabric under the action of the elastic recovery force generated by the internal stress, the crease bending of the fabric begins to recover, that is, the Angle of the crease recovery begins to increase. The crease recovery Angle increases with time, and its change is similar to that of material creep. In this process, in addition to the elastic recovery force of the fabric, it is also affected by friction resistance. The friction resistance is caused by the relative slip between yarns and between the fibers of the yarn, and its direction is opposite to the elastic recovery force. When the elastic recovery force and friction resistance of the fabric are balanced, the fabric achieves the maximum recovery effect, and the fabric fold Angle is the crease recovery Angle of the fabric.
Factors influencing crease recovery performance
The crease recovery of fabric depends on the relative balance between the elastic recovery force and the friction resistance. The greater the restoring force, the smaller the internal friction resistance of the fabric, the better the crease restoring performance of the fabric. Generally, the elastic resilience of the fabric depends on the inherent properties of the fabric fibers, and the elastic resilience of different fibers is different, such as the fabric made of wool and polyester fibers, which has better crease recovery performance. At the same time, the raw material composition and twist of the fabric have an impact on the crease recovery performance of the fabric, taking the thin worsted fabric as an example:
Fabric ingredient
Because the elastic recovery of polyester fiber is higher than that of wool, a certain amount of polyester fiber mixed in wool can improve the crease recovery performance of fabric, and the higher the content of polyester fiber, the better the crease recovery performance of fabric.
Fabric twist
The twist of a yarn has a similar effect on its strength. In a certain range, the crease recovery of fabric is enhanced with the increase of yarn twist coefficient. When the twist exceeds a certain value, the crease recovery of fabric decreases with the increase of yarn twist coefficient. This is because when the twist is too low, the fibers in the yarn are loose, and under the action of external forces, the fibers are prone to excessive slip, which is mostly irreversible. This creates creases on the surface of the fabric. When the twist is too high, the yarn fiber produces a large torsion deformation, its plastic deformation increases, and the fiber is tightly bound. After the removal of the external force, the relative movement of the fibers and the degree of recovery are reduced, and the creases generated on the fabric surface are not easy to fade.
The crease recovery performance of fabric is also influenced by temperature and humidity conditions, making it challenging to restore creases when subjecting the fabric to high temperatures and high humidity levels. Moreover, resin finishing enhances the intermolecular cross-bonding within the fabric’s molecular chains, thereby improving its ability to recover from stretching deformations and enhancing its crease recovery performance. Additionally, dyeing, finishing processing, and heat setting can further enhance the crease recovery performance of fabrics.
Crease recovery test
There are many methods to measure the crease recovery of fabric, but the most common is to measure the crease recovery Angle of folded fabric samples. The method is to fold the fabric sample of specified shape and size under certain atmospheric conditions and pressurize it for a certain time, and then measure the Angle of fabric recovery after weight release. According to the position of the crease line of the sample of return Angle, it can be divided into horizontal method and vertical method.
Horizontal method: when the sample crease recovers, the crease line is parallel to the horizontal plane, and the method of measuring the recovery Angle;
Vertical method: When the sample crease recovers, the crease line is perpendicular to the horizontal plane, and the method of measuring the recovery Angle.
The steps are as follows: the pressure load on the sample is folded at 10 N, the pressure time is 5 min, and the slow crease recovery Angle of the sample is measured at 5 min after the pressure load is removed.
Fabric crease recovery tester
Fabric crease recovery tester is used to determine fabric recovery ability after being creased an indicated with crease horizontal method. This tester is suitable for fabrics with various kinds of thickness, and can get fast and slow crease recovery index under room environment.
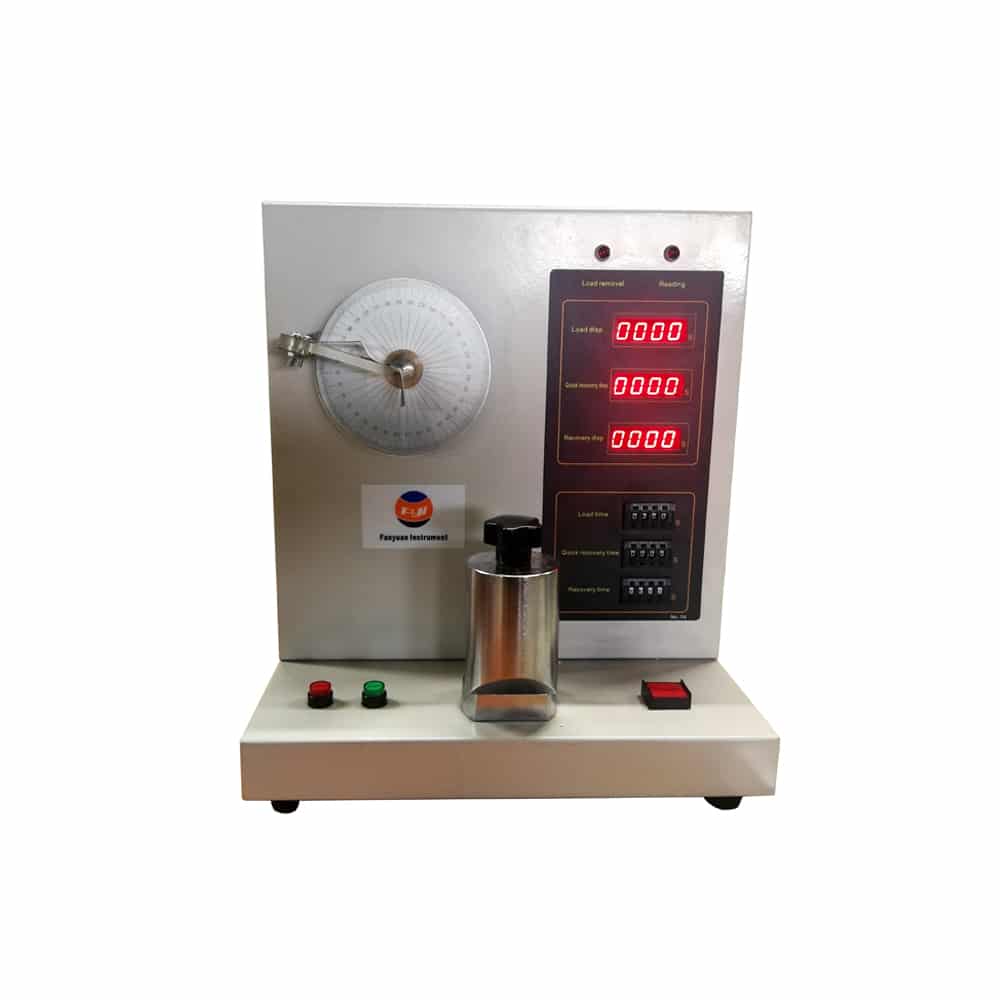

It adopts horizontal method to measure crease recovery ability of fabric,
Test process can be carried on automatically, and with alarm to remind operator.
Fabric crease recovery tester complies with GB/T 3819, AATCC 66, ISO 2313, JIS L1059,KS K0550, K0551, K055, BE EN22313 etc. international and retailer standards.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

See how the author skillfully weaves together facts, anecdotes, and personal reflections in each post.