
Introduction of Gill Box Machine
One of the most significant pieces of equipment in the long fiber processing system, such as worsted wool spinning, is the gill box machine. Because the fiber straightening parallelism and evenness of the slivers generated by the roller carding machine do not match the spinning criteria, some of them still have the “hook” phenomenon and cannot be spun directly in the long-staple spinning system. As a result, the top is processed and transformed using a gill box machine.
The gill box machine carding process is a crucial step in the wool spinning process. The purpose is to improve the parallel stretching degree of the fibers and improve the structure of the sliver through merging. The working state of the gill box has a very close relationship with the output and quality of worsted wool spinning.
Contents
The main tasks of gilling process
- Several merging and drafting improved the homogeneity of medium and long sliver parts;
- Straightening parallelism and fiber separation are increased further by combing the needles, and hooks and curls are removed.
- The fibers are blended uniformly and the yarn quality is maintained by repeated merging and drafting.
- Eliminate any minor impurities and short hair.
Types of gill box
There are many different types of gilling machines used in the worsted wool spinning processing system today.
They are classified based on the transmission mode of the needle plate and the device for controlling fibers in the drafting area. Screw type gilling machines, chain type gilling machines, rotary type gilling machines, toothed roller type gilling machines, and needle plate free drafting machines are the most common.
According to the installation arrangement of the needle board, it can be divided into three types: open type, cross type and half cross type.
Structure of gilling machine
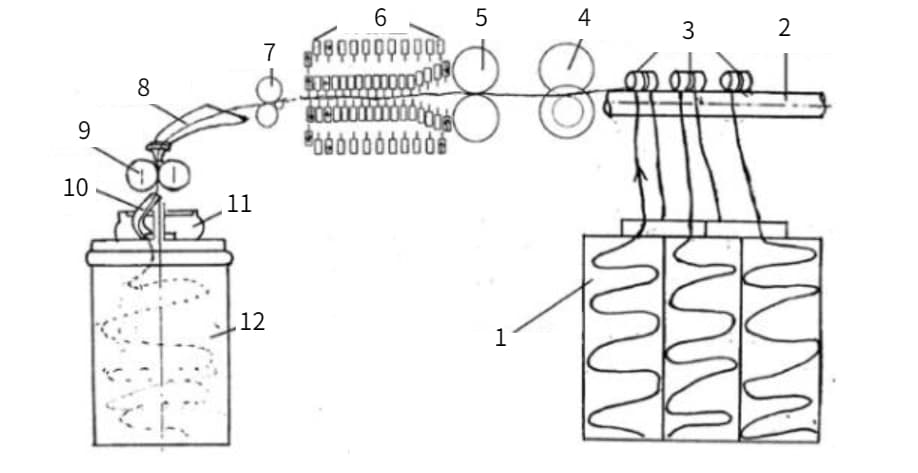
1.Feeding can 2. Guide roller 3. Guide roller 4. Measuring roller 5. Middle roller 6. Needle plate area 7. Front roller 8. Arc guide 9. Compression roller 10. Inclined tube for coiling 11. Coiler 12. Output can
There are many types of gilling machines, but their composition is roughly the same, mainly composed of feeding mechanism, drafting mechanism, pressurizing mechanism, coiling mechanism, and autoleveling device.
Feeding mechanism
It is mainly composed of sliver table, sliver roller, sliver rod and guide sliver assembly plate, etc., where multiple wool tops are merged to mix and improve wool top unevenness.
Drafting mechanism
It is mainly composed of front, middle and rear rollers, compacting rollers and needle comb boxes. Among them, the needle row mechanism is more complicated, including parts such as needle plate, screw rod, beater, pressure plate and guide rail. The function is to draw the combined raw materials finely, and at the same time improve the straightening parallelism of the fibers.
Pressurizing mechanism
The two tasks of pressurizing the front roller and lifting the comb box can be completed respectively through the conversion of the valve.
Coiling mechanism
It is mainly composed of a coiling plate, a small pressure roller, a can chassis and a can, and its function is to make a sliver that meets certain specifications.
Autoleveling device
In the wool processing system, there is usually equipped with a final gilling machine equipped with an autoleveling device, which is purely mechanical. The main function is to automatically change the draft ratio after detecting the thickness change of the fed sliver, thereby actively and effectively improving the uniformity of the output sliver and improving the quality of the finished sliver.
Process of gill box
The process of gill box is similar to that of the draw frame, except that the carding box mechanism is added to the drafting device.
Several slivers are pulled from the can and stacked side by side on the bar guide table to create fiber sheets before entering the rear roller after passing through the bar guide roller and bead roller, respectively.
After being somewhat drafted by the middle roller, the sliver enters the cross needle plate region and is drawn in a circular motion by the front roller by the upper and lower needle plate holding belts to finish the drafting and carding. To achieve progressive carding, the top and lower needle boards gradually enter the fiber layer.
The fibers drawn and output by the front roller are collected into a sliver by the bundler and the compacting roller, and finally coiled and placed in the output can regularly by the coiling disc and the coiling inclined tube.
Technical parameters of the gilling machine
| Feed mode | Platform or elevated |
| Drive mode of chain plate | Double line screw, double head beater |
| Number of need plate | 88 |
| Max. times of beating | 800 |
| Draw type | Single zone cross need plate drawing |
| Draw ratio | 2.5-15 |
| Doubling | 3-6 |
| Max. feed quantity | 60g/m |
| Output sliver speed of front roller | 0-50m/min |
| Output silver type | Platform or form sliver |
| Auto-stop device | Door cover auto-stop |
Defect causes and solutions
| Possible Causes | Solutions | |
| Evenness uneven | The drafting ratio or the front gauge of the carding machine is set too large; Bad joint; The pressure of the front roller is unstable; Needle plate and roller fluff or defect. | Adjust the drafting process; Specification connector; Strengthen equipment rectification. |
| Uneven weight | Improper matching of feeding sliver or broken sliver and lack of roots; Roller pressurization is uneven. | Adjust the number of feeding roots and strengthen the tour; Adjust roller pressurization |
| Hair grain increase | Needle board steel needle bending belt hook, steel needle defect, etc.; The draft ratio of the head needle and the second needle is too large; Top channel is not clean and smooth. | Strengthen maintenance; Adjust the draft ratio; Clean up carefully. |
| Slivers hairy | Less oil, lower moisture regain, high static electricity, poor fiber cohesion; The top channel hangs wool. | Increase the amount of oil and antistatic dosage; Clean the top channel. |
| Draft hard ends in the sliver | Excessive tension in the posterior region; Fiber length is too long;High friction on the fiber surface; Top twisting and overlapping feeding; Insufficient roller pressure, etc. | Reduced back tension draft; Increase the front gap; Regulate user operations; Increase front roller pressure. |



Your words truly resonate with me on a personal level.
You have a natural talent for blogwriting.
Your writing style is both informative and entertaining.
Those anecdotes you shared in your latest blog post really added a personal touch and made it all the more engaging.
When I read your blog, I can feel your passion for the topic shining through.