
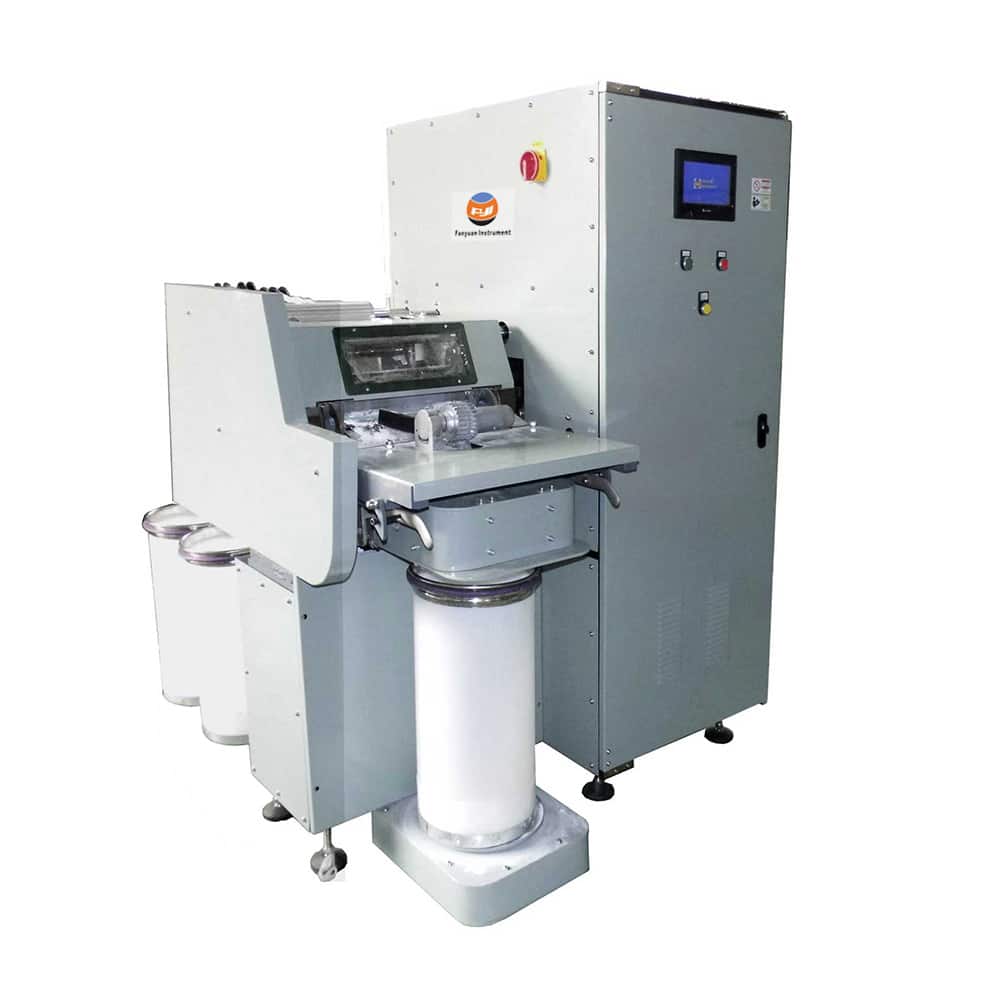
Summary of Comber Machine Related Questions
Contents
What is the meaning of comber machine?
Before delving into the meaning of comber machine, it is necessary to first define combing. Combing is one of the processes used in the spinning process to exclude shorter fibers and remove kinks (neps, hair particles, grass clippings, cocoon skin, and so on) in the fibers. Simultaneously, the fibers are straightened and paralleled further, resulting in a combed sliver of relatively uniform thickness. The combing machine is the machine that performs the combing process during the spinning process.
What is comber machine used for?
Comber machine is useful in the textile industry, particularly for companies that want to produce high-quality yarns and fabrics. These companies need to produce high-quality yarns and fabrics with high strength, softness, and gloss. Combing machines, in addition to the textile industry, can be used in other fields that require the separation and processing of impurities, such as cotton processing in agriculture. Furthermore, combing machines can be used for teaching and research at some universities and research institutes.
Types of comber machine
It is classified into two types based on its structure: straight comber and circular comber. The straight comber is currently the most popular. Straight combers are ideal for processing fine and short fibers, and they feature intermittent and periodic combing. Furthermore, it has a better effect of eliminating impurities, neps, wool, and hemp, as well as a lower combing noil rate and a relatively low output.
How the combing machine works?
Holding and combing are the essence of combing, and they can effectively remove short fibers, small impurities, and improve fiber straightening and parallelism. Although there are many different types of straight combers, their basic working principles are the same. That is, the two ends of the fiber bundles are separated and combed on a regular basis; the cylinder combs the head end, and the top comb passively combs the rear end, and the combed fiber bundles are poured into the fiber web in the machine separately (drawing) Splicing (lapping), and then the fiber web is output outside the machine.
Comber machine function
Exclude linters
Exclude short fibers shorter than 16mm (or shorter than 12.7mm) to increase the average length and regularity of cotton fibers, improve yarn uniformity and strength, and reduce yarn hairiness and thickness.
When the noil rate is 12%-18%, the manual detection method removes short fiber at a rate of 42%-48%; machine detection removes short fiber at a rate of 40%-70%.
Eliminate neps and impurities
Remove neps, minor impurities, and faults with fibers, and minimize the amount of neps and impurities on the yarn’s surface to improve the fabric’s visual quality.
When the noil rate is 12%-18%, the elimination rate of neps by manual detection is 10%-20%. When the combing noil rate is 15%-19%, the neps removal rate by machine detection is 65%-85%.
Impurities are removed at a rate of 50%-60%.
Improve fiber separation, straightness and parallelism
Increase the separation degree, straightness, and parallelism of fibers in tiny rolls to enhance the internal quality of the combed sliver, consequently boosting the strength, evenness, and shine of the yarn.
It can also limit the formation of neps during the succeeding process’s drafting.
Before combing, raw sliver has a fiber straightness of 55%-65%, whereas combed sliver has a fiber straightness of 90%-95%.
Comber structure
Feeding part
The lap roller and the cotton feeding roller are the major components of the feeding section, and the surface has thick and narrow grooves. The cotton feeding roller is fitted on the bottom nipper, and the nipper swings back and forth once to produce a 4-6.5 mm cotton layer (customarily called cotton feeding length or feeding length). Its purpose is to feed the cotton layer on a regular and quantitative basis.
Nipper
The jaws are little arcs that match each other, and there are two upper and lower nippers. The forward and rear swing of the nipper is controlled by the headstock’s linkage system, and the opening and closing of the top nipper is limited by the linkage mechanism. The top nipper has a pressure mechanism, and the distance between the nipper lip (when closed) and the cylinder comb needle varies with the swing of the nipper, with the tightest section measuring 0.3-0.5 mm.
Comb part
The carding mechanism of the combing machine consists mostly of the combing cylinder and the top combing mechanism, which is the most significant portion of the combing machine and plays a critical role in combing quality.
Cylinder
The cylinder is made up of a smooth curved plate (bow plate) and a grooved curved plate (also known as the needle plate seat), each of which accounts for half of the curved surface of the cylinder. 14 to 17 needle plates (about a fourth of the cylinder’s total arc surface) are implanted in the slot of the grooved arc plate. The needle board is planted with combing needles, which vary in thickness and density according on the variety being spun. The cylinder shaft goes through the entire machine, and there is an index plate at the end of the shaft that serves as the benchmark for all of the machine’s motions (timing positioning).
The major carding component of the combing machine is the cylinder. Its primary role is to comb the majority of the length of the front and middle fiber bundles from shallow to deep, allowing the fibers to be more straightened, parallelized, and separated, and the hair bundles to be deleted. Noil is formed by linters, neps, and other impurity faults in the fabric.
Top comb
Top combs are classified into two types: swing and fixed. It features a plate construction with needle rows on the bottom border. The needle row’s working width is the same as the cylinder’s breadth. Combing needles are typically flat.
The top comb is in charge of combing the ends of the beards combed by the cylinder’s end. Holding combing also includes beard combing with the top comb. The needle gap of the top comb goes through, allowing the top comb to comb the tail end of the tuft of hair.
Separation roller
Separation joining is the process of realizing periodic combination and separation of front and rear fiber layers and continuous output of cotton web. Good joint quality is an effective guarantee for improving product quality.
If anyone has any other questions about the comber, feel free to discuss it in the comments section.



Your blog is a place where I always feel welcome and accepted.
Your writing always puts me in a good mood. You have a gift for spreading positivity.
Your blog is a reminder that the little things in life are often the most important
A blog like this is a treasure trove of knowledge, waiting to be explored.